Rіvnyannya schodo function is given implicitly. Alignment of dotic and normal to the graph of the function. The main power of the undefined integral
Pokhidnoy programs.
5.1.Geometric zmil pokhіdnoy:
Let's look at the graph of the function y= f (x).
From little one 1 it is clear that there are two points Aі B graphic function: , de α - cut badly sichno AB.
In this rank, the retail price is more expensive than the cut coefficient of the sichno. How to fix a point A and rush straight to her point B, then it changes unconditionally and approaches 0, and AB approaching dotty AC.
Also, between the retail price is more expensive than the cut coefficient of the dot at point A, then. . Sounds are screaming: Pohіdna function x 0 is more expensive than the cult coefficient dot to the graph of the function y = f(x) at the tsіy point, then. .
1. The position of the graph of the function at the point (x 0; f (x 0) is called the boundary position of the sichno (AC).
Rivnyannya dotichny : y – f(x 0) =
2. A straight line perpendicular to the dot (AC) at the point (x 0; f (x 0), is called the normal to the graph of the function.
Normal alignment: y – f(x 0) =
Manager: Add the alignment of the dot and the normal drawn to the graph of the function y=10x-x at the point with the abscissa, which is equal to x 0 =2.
Solution:
1. We know the ordinate of the dotik point: f (x 0) \u003d f (2) \u003d 10 ∙ 2–2 2 \u003d 16,
2. We know the top factor of dot: f "(x) = (10x-x)" = 10-2x, = f"(2)=10–2∙2=6
3. Folding dotty equalization: y–16 = 6∙ (х-2), y–16 = 6х–12, y–6х–4 = 0 – dotary equalization,
4. Adding normal alignment: y -16 = , 6y -96 = -x + 2, 6y + x -98 = 0 - normal alignment.
5.2. Physical changer:
Appointment. The speed of the rush of the body is fresher than the first wind of the way by the hour:
5.3. Mechanical changer of the following:
Appointment. The speedy rush of the body is more expensive the first windy wind after an hour, or the other windy way after an hour:
Manager: Signify the speed of that accelerated point that collapses backwards according to the law at the moment t=4c.
Solution:
1. We know the law of speed: v= S"=
2. We know the speed at the moment t = 4c: v(t) = v(4)=2∙4 2 +8∙4=64 one/sec
3. We know the law of speed: a=v′=
4. We know the acceleration at the moment t \u003d 4c: a(t) = a( 4)=4∙4+8=24one/sec 2
ROZDIL 1.3. Differential function and yogo zastosuvannya at the nearest calculations. Understanding the differential function
Function differential y \u003d ƒ (x) at point x, the main part of the її increase is called, equal to the addition of a function similar to the increase in the argument, i is designated dу (or dƒ (x)): dy \u003d ƒ "(x)∙∆х(1).
Differential du called so differential of the first order. We know the differential of the independent variable x, so the differential of the function y = x.
Since y "=x" = 1, then, according to formula (1), it can be dy = dx = ∆x, so the differential of the independent change is more expensive for the increase in the change: dx = ∆x.
Therefore, formula (1) can be written as follows: dy \u003d ƒ "(x) ∙ dx(2) in other words, the differential function is more expensive to supplement a similar function. the differential is an independent change.
From the formula (2) the equality dy / dx \u003d ƒ "(x) is evident.
Butt1: Know the differential of the function ƒ(x)=3x 2 -sin(l+2x).
Solution: Behind the formula dy \u003d ƒ "(x) dx we know dy \u003d (3x 2 -sin (l + 2x))" dx \u003d (6x-2cos (l + 2x)) dx.
Butt2: Change the differential to a different order of the function: y = x 3 -7x.
Solution:
ROZDIL 1.4. Primary. Integr. Calculation methods unassigned integral.
Appointment 1. The function F(x) is called the primary function for the function f(x) on the current interval, the differential of which is the opposite of f(x)dx. butt: f(x) = 3x2 3x2 dx F(x) = x3.
However, the differential of the function is not the only one, but the impersonal one. Let's look at the butt: F 1 (x) \u003d x 3, F 2 (x) \u003d x 3 + 4, F 3 (x) \u003d x 3 - 2, at a glance F (x) + Z, de Z is quite a constant. Mean for the function f(x)= 3x 2 to establish the impersonal primary ones, which are considered one kind of one with a permanent addition.
Appointment2. The impersonality of all primary functions f(x) on the first interval is called the non-significant integral of the functions f(x) on the same interval and is denoted by the symbol f(x)dx .
The whole character is read like this: "integral from f(x) to dx", with such a rank for the appointment:
∫ (x)dx = F(x)+C.
Symbol ∫ is called the integral sign, f(x) is the integrand function, f(x)dx is the integrand virase, x is the change integration, F(x) is the first,
C - fast.
The main power of the undefined integral:
1. The differential of an undefined integral is more like a pintegral virase, that is.
d ∫ f(x)dx = f(x)dx.
2. Inconsistency of the integral in the differential of the function of a healthy function, folded from a fairly constant: ∫ d F(x) = F(x) + C
3. A constant multiplier can be blamed for the sign of the integral: ∫ kf(x)dx = k ∫ f(x)dx, k-const.
4. Non-values of the integral in the form of the algebraic sum of the functions of the healthy sum of the integrals in the form of the skin of them: ∫ (f 1 (x) + f 2 (x) -f 3 (x)) dx = ∫ f 1 (x)dx + ∫ f 2 (x)dx – ∫f 3 (x)dx .
Topic : Understand well and normal.
Equal dot and normal.
Qile:
Subject: cognize students with understanding: that normal is dotichna to the curve; close the data of understanding at the hour of the order of the day on the folding of the dot and the normal; z'yasuvati, what kind of power can kutovі koefіtsієnti dotichї and normal.
Communications: argue your point of view, compare it to your position in a way that is not predictable for your opponent; vmіti hear that slightly one of one.
Knowledge : to establish causal and inherited connections; express the sensory situation in different ways (little pieces, symbols, diagrams, signs).
Regulatory: take the funeral meta, save the first hour of the beginning of the day, regulate the whole process of the celebration and clearly celebrate the victory of the memorial task.
Features: shaping the awareness of interest to the emergence of a new one, motivation to self-sufficiency and collective action.
Lesson Hide:
1. Updating the basic knowledge of students:
(Introduction to understand how and normal to curve)
We know the analytical and physical change of a similar one: (selected students :
analytical change - tse, physical - tse security of the process specified by the function).
Z'yasuєmo geometric zmіst pokhіdnoї.
For whom, we introduce the understanding of how the curve is in this point.
From the high school course of geometry, you know how to understand the stake. (selected students : dotichna up to the stake is shown as a straight line, which lies in the same plane with a column and can be a single point with it).
However, the designation of the dot can not be stagnant for a free curve. For example, for the parabola, the axes may one by one sleeping point with a parabola. However, all is dotichnoy to a parabola, and all - no. Damo the curve at these points.
Come on - deyaki points of a dovilnoy curve - a curve, so what. When approaching a point along the curve, turn around the point
Appointment. The boundary position of the sіchnі with non-closed proximity points along the curves is calleddotic to the curve to the point
Appointment . Normallu to the curve at the point is called a straight line, which passes through the point perpendicular to the dot to the curve at the tsij point.
Yakshcho - dotichna to the crooked point,
then it will be perpendicular to the normal to the curve at the point
Explanation of the new material:
(For good reason, why do you have a geometrical zmist , Yaku power mayut kutovі koefіtsієnti dotichї i normalі).
Let the curve є graph function. Krapki
lie on the graph of the function. Straight - dotichnaya to crooked.
Kut nakhil dotichno
Pokhіdna function in the point of the tangent of the kuta nahil dotic, carried out in the point or the kuta coefficient, which is the graph of the function in the tsіy point .
Rivnyannya dotichny to the curve at the point may look
Equation of normal to the curve at the point may look
(3)
Problem nutrition : to marvel at the dotality and normality, why is it worthy and similar?
Why do you love TV? Why so vіdbuvaetsya?
(Students are responsible for giving the same answer to the power supply: -1, the scales are correct and the normal is mutually perpendicular)
Consolidation of theoretical material in practice:
( Appreciation in the auditorium)
EXAMPLE 1. Calculate the kutovі coefіtsієnti, scho suyuyutsya parabolas at the points.
Solution. From the geometric value of the tail (formula 1) the top coefficient of the dot.
We know the following functions: .
. Father, .
We know the value of the similar point
Father, .
EXAMPLE 2. At the parabola, the dots are drawn at the points Know the cuts are slightly dot to the Ox axis.
Solution. Behind the formula (1)
We know. .
Let's calculate the value of the similar point: .
Father, in
Similarly for points.
Father, i
EXAMPLE 3. In a certain point it is dotichnaya to the crooked, heeled to the axis Ox
under the hood
Solution. Behind the formula (1)
; . Father, i
Substituting a function, we take it away. They took a speck.
EXAMPLE 4. Fold the alignment of the dot and the normal to a parabola at the point
Solution. Rivnyannya dotichny to crooked may look.
Іz wash the task. Let's get lost.
; .
Substituting all the values in the equal, we take away the equal of the dot.
or.
We fold the normal, speeding up the formula:
or
Task for independent vision:
1. Know the cutoff coefficient of dot, carried out to the curve in points.
2. The curve is set to the level of the line. Designate the cut to the point where there is a positive straight line of the axis, drawn to the curve at the points at the points behind the abscissas.
3. Find a point on a curve, a straight line is parallel to a curve.
4. At any point dotichna to the curve: a) parallel to the axis; b) utvoruє z vіssu kut 45?
5. Find the abscissa of the point of the parabola, in which case it is parallel to the abscissa axis.
6.Know the cut coefficient of dot, carried out to the curve in points.
7.Which point is dotichna to crooked utvayuє z vіssyu kut 30?
8.At the same point, it is up to the schedule of the function utvoryu kut 135
from the vіssu?
9.Which point is the graph of the function parallel to the x-axis?
10. At some points, the apical coefficient of the dotic to cubic parabola is more than 3?
11. Know the cut of the sickly dot to the crooked point, the abscissa is more expensive 2.
12. Fold the alignment of the dot to a parabola at the point of the abscissa
13. Fold the dot to hyperbole at points
14. Fold the alignment of the dot to the curve in the dots.
15. Know the dot to the curve at the point of the abscissa.
Vіdpovіdі : 1) .12 2). 45°arctg 5 3) .(1;1) 4) .(0;-1) (0,5;-0,75) 5) .1/2 6) .1 7) .(/6;61/12) 8) .(0:-1) (4;3) 9) .(0;4) (1;-5) 10) .(1;1) (-1;-1) 11) . 45°12) .y = -2x-113) .y = -x +214) .y=4x+615) .y = 4x-2.
Evaluation criterion : "5"- Day 15
"four"- 11-14 zavdan
"3"- Chapter 8
4. Pouches for the lesson : grading; + i - a lesson for the student
5. Home tasks: prepare for the inquiry:
Give the definition dotichny to the crooked.
What is called the normal to the curve?
Why do you have a geometrical edge? Write down the formula.
Record the alignment of any curve in the given point.
Write down the alignment of the normal to the curve at this point.
Answer tasks 1-15 on the choice of evaluation criteria;dodatkovo for bajannyam : fold and verse a card on this topic.
Stosovna is straight , Should the graph of the function be at one point and all points that are on the smallest line in the graph of the function. That is why it is dotichna to pass through the schedule of the function under the first line and cannot pass through the dotik point of the sprat of dotik under the other cuts. The equalization of the dot and the equalization of the normal to the graph of the function are added up for the additional help.
The alignment of the dot is to be derived from the alignment of the straight line .
We show the alignment of the dot, that buv is the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function.
y = kx + b .
in the new k- Cut coefficient.
Please note the upcoming entry:
y - y 0 = k(x - x 0 ) .
The meaning of the f "(x 0 ) functions y = f(x) at the point x0 to the cut coefficient k=tg φ equivalent to the graph of a function drawn through a point M0 (x 0 , y 0 ) , de y0 = f(x 0 ) . Whom do you think geometrical shift .
In this manner, we can replace k on the f "(x 0 ) and take it further equalization of the dot to the graph of the function :
y - y 0 = f "(x 0 )(x - x 0 ) .
In the tasks of the folding, it is necessary to bring the equalization to the graph of the function (and we will soon move on to them) straight at the savage look. For which it is necessary to transfer all the letters of that number to the left part of the equal, and leave zero on the right part.
Now about the equalization of the normal. Normal - it is straight, so as to pass through the torsional point of the graph of the function perpendicularly to the dot. Equation of normal :
(x - x 0 ) + f "(x 0 )(y - y 0 ) = 0
For a warm-up, the first butt is taught independently, and then we marvel at the decision. Let's all imagine that for our readers it won't be a cold shower.
butt 0. Fold the alignment of the dot and the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function at the point M (1, 1) .
example 1. Fold the alignment of the dot and the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function ![]() , which is the abscissa of the torsional point.
, which is the abscissa of the torsional point.
We know the following functions:
Now we have everything that is necessary to present in the theoretical proof of the record in order to take into account the exactness of the dot. Acceptable
![]()
We were spared for this butt: the top coefficient turned out to be equal to zero; Now we can add and equalize the normal:
![]()
A little lower: a graph of the function of a burgundy color, what to do green color, the normal of the orange color.

The offensive butt is also not folding: the function, like in the front, is also a rich member, but the cut coefficient is not equal to zero, that will get one more crochet - bringing it up to a wild look.
butt 2.
Solution. We know the ordinate of the dochi point:
We know the following functions:
![]() .
.
We know the value of the torsion point at the point of torsion, that is the apex coefficient of the dot:
Submitting all the omitted data from the "formula-blank" and at least equal dot:
![]()
It is brought up to a scatter look (all letters of that number, in the form of zero, are taken in the left part, and zero is left in the right part):
We add the equalization of the normal:

example 3. Fold the alignment of the dotic and the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function, like the abscissa of the point of the dotic.
Solution. We know the ordinate of the dochi point:
We know the following functions:
![]() .
.
We know the value of the torsion point at the point of torsion, that is the apex coefficient of the dot:
![]() .
.
We know the equal dot:
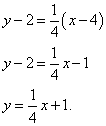
Before that, in order to bring the level to a savage look, it’s necessary to “comb” the trifles: multiply term by term by 4. Robimo tse and lead to a savage look:
We add the equalization of the normal:

butt 4. Fold the alignment of the dotic and the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function, like the abscissa of the point of the dotic.
Solution. We know the ordinate of the dochi point:
![]() .
.
We know the following functions:
We know the value of the torsion point at the point of torsion, that is the apex coefficient of the dot:
![]() .
.
Otrimuemo equal dotica:
We direct rivnyannya to a slanderous look:
We add the equalization of the normal:
![]()
The pardon has been expanded with folding equals of dot and normal - do not remember that the function is given in the application - folding and counting її like a simple function. Step on butts - already s collapsible functions(Vіdpovіdny lesson vіdkriєtsya in a new vіknі).
Example 5. Fold the alignment of the dotic and the alignment of the normal to the graph of the function, like the abscissa of the point of the dotic.
Solution. We know the ordinate of the dochi point:
Respect! This function is collapsible, but the argument to the tangent (2 x) itself is a function. To that we know the func- tions like the folding func- tions.



