Kut mizh two direct formulas. Cut between straight lines on the flat. Canonical straight lines
KUT between flats
Let's take a look at two planes α 1 and α 2 tasks in the same way:

Pid cutom between two flats, one of the two-faced kutіv, made up of these flats, is comprehensible. It is obvious that between normal vectors and planes 1 and 2 is equal to one of the designations of sum dihedral ![]() . Tom
. Tom  . Because
. Because ![]() і
і ![]() , then
, then
 .
.
butt. Designate a cut between the flats x+2y-3z+4=0 and 2 x+3y+z+8=0.
![]()
Wash the parallelism of two planes.
Two planes α 1 and α 2 are parallel to each other and only to the same, if they are normal vectors and parallel, and also ![]() .
.
Also, two planes are parallel to one to the same and less to the same, if the coefficients for the corresponding coordinates are proportional:
![]() or
or
Wash the perpendicularity of the planes.
It was clear that two planes are perpendicular and the same, if they are normal vectors and perpendicular, either.
In such a manner,
apply.
DIRECTLY IN SPACE.
VECTORNE RIVNYANNYA DIRECTLY.
PARAMETRIC LEVELING DIRECT
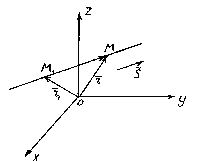
The position of the straight line in the space is completely dependent on the given data, as there are її fixed points M 1 i vector , parallel to the straight line.
Vector, parallel line, is called direct the vector is straight.
Otzhe, hi straight l pass through a point M 1 (x 1 , y 1 , z 1), which lies on a straight line parallel to the vector.
Let's look at a certain point M(x, y, z) on a straight line. From the little one you can see that ![]() .
.
Vectors and kolіnearnі, so there is such a number t, sho , de multiplier t you can pick up whether it is a numerical value in the fallow in the position of the point M on a straight line. Multiplier t called a parameter. Assigning the radius-vector point M 1 ta M evidently through i, otrimuemo. Tse equal is called vector straight lines. It shows the value of the parameter to the skin t change the radius-vector of the deac point M, which lie on a straight line.
Let's write down the order of the coordinate form. Respectfully, sho, ![]() and stars
and stars
Otrimani equals are called parametric straight.
When changing the parameter t coordinates change x, yі z i mottled M move in a straight line.
CANONIC RIVNYANNYA DIRECT

Come on M 1 (x 1 , y 1 , z 1) - a point that lies on a straight line l, і ![]() - Її direct vector. I'll take it straight to the full point M(x, y, z) i look at the vector.
- Її direct vector. I'll take it straight to the full point M(x, y, z) i look at the vector.
It was clear that the vectors and collinear, to that their respective coordinates may be proportional,
![]() – canonical straight lines.
– canonical straight lines.
Respect 1. Respectfully, the canonical alignment of the straight line can be taken away from the parametric ones by turning on the parameter t. True, from parametric equals it is necessary ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
butt. Write straight lines ![]() parametric look.
parametric look.
Significantly ![]() , stars x = 2 + 3t, y = –1 + 2t, z = 1 –t.
, stars x = 2 + 3t, y = –1 + 2t, z = 1 –t.
Note 2. Let the straight line be perpendicular to one of the coordinate axes, for example, the axis Ox. Then a direct vector of lines of perpendiculars Ox, otzhe, m=0. Otzhe, parametric equalization of the direct look forward
Including equalization parameter t, Take away straight from the sight

Prote and at the same time let us formally write down the canonical equalities of the direct yak ![]() . In this order, if there is zero in the banner of one of the fractions, then it means that the straight line is perpendicular to the dual coordinate axis.
. In this order, if there is zero in the banner of one of the fractions, then it means that the straight line is perpendicular to the dual coordinate axis.
Similarly, canonical equals ![]() straight line is perpendicular to the axes Oxі Ouch or parallel to axis Oz.
straight line is perpendicular to the axes Oxі Ouch or parallel to axis Oz.
apply.
ZAHALNI RIVNYANNYA DIRECT, YAK LINE REVERSION OF TWO PLANES
Through the skin straight in the open space to pass an impersonal area. Be it two of them, intertwining, they signify in space. Otzhe, if there were two equal flats, which are looked at together, they are equal to the straight lines.
Vzagali be-like two not parallel planes

designate a straight line. Qi equal are called wild jealousy straight.
apply.
Prompt straight, set by peers ![]()

To encourage direct it is enough to know whether there are її points. Easiest way is to choose the crosspoints of the straight line with the coordinate planes. For example, a cross point with a plane xOy we take it straight, vvazhuchi z= 0:
Virishivshi tsyu system, we know the point M 1 (1;2;0).
Similarly, respectfully y= 0 xOz:
![]()

From the upper levels of the straight line, you can go to the її canonical or parametric levels. For whom it is necessary to know some point M 1 on a straight line and a direct vector is a straight line.
Point coordinates M 1 is taken from the center of the equalization system, having pressed one of the coordinates to a sufficient value. For a direct vector question, it is important that the vector can be perpendicular to both normal vectors. ![]() і
і ![]() . To that for the direct vector l can you take vector witwear normal vectors:
. To that for the direct vector l can you take vector witwear normal vectors:
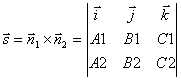 .
.
butt. Lead galnі rivnyannia straight ![]() to the canon look.
to the canon look.
Let's find a point that lies on a straight line. For which we choose only one of the coordinates, for example, y= 0 and split the equalization system:
![]()
Normal vectors of planes, which define a straight line, determine coordinates. ![]() Therefore, the direct vector will be direct
Therefore, the direct vector will be direct
 . Otzhe, l:
. Otzhe, l: ![]() .
.
KUT MIZH STRAIGHT
Kutom between straight lines in the space we will call whether one of the summary kutivs, made two straight lines, drawn through a certain point in parallel, we give.
Let the space set two straight lines:
It is obvious that kut between їх straight lines can be taken as kut between їх direct vectors i . So yak, then for the formula for the cosine kuta between vectors we take
The Danish material of devotions to such a concept, like a cut between two straight lines, that intertwine. At the first point, we explain what we represent, and show it in illustrations. Then let's analyze, as you can know the sine, cosine of that kut and the kut itself (we can look at the fluctuations with a flatness and trivimirny space), we will need formulas and show them on butts, like the stench itself will be in practice.
In order to understand what a cut is, what is settled when two straight lines are crossed, we need to guess the very designation of the cut, the perpendicularity and the cross point.
Appointment 1
We call it two straight lines that intertwine, as they have one bright point. Tsya point is called a point of crossing of two straight lines.
The skin is directly podіlyaєtsya with a point of peretina on the promenі. Offenses are straight with which 4 kuti are satisfied, of which two are vertical, and two are sum. If we know the world one of them, then we can name the others.
It is acceptable, we see that one of the kutiv dorivnyu α. In such a case, which is vertical in relation to the new one, it is also more advanced α. In order to know the kuti that we have lost, we need to calculate the difference 180 ° - α. If α is closer to 90 degrees, then all cuts will be straight. Lines, which are intertwined under a straight cut, are called perpendicular (the concept of perpendicularity is assigned to the article).
Look at the little ones:
Let's move on to the formulation of the main purpose.
Appointment 2
Kut, the two straight lines that mingle, - the lesser world of 4 kutivs, like two straight lines.
From the point of view, it is necessary to grow an important visnovok: rozmir kuta in any way there will be expressions, be it day number in the interval (0, 90) If straight lines are perpendicular, then cut between them in some kind of fall to 90 degrees.

Vminnya knows the world of kuta between two straight lines, which are tinkering, corny for the accomplishment of a wealth of practical tasks. The variant method can be chosen from a number of options.
On the other hand, we can take geometric methods. As we are aware of the dodatkovі kuti, then we can tie them to the kut we need, vikoristovuyuchi power equal or similar figures. For example, since we know the sides of the tricot and it is necessary to calculate the cuts between the straight lines, on such rasterizations of the sides, then for the sake of perfection we need the cosine theorem. Since we have a straight-cut tricouter, then for pidrachunks we also need to know the sine, cosine and tangent of the kuta.
The coordinate method is also more convenient for executing tasks of this type. Let's explain how yogo vikoristati is correct.
We have a rectangular (Cartesian) coordinate system O x y, in any task there are two straight lines. Significantly їх letters a and b . Directly at one's own, one can describe with help whether one is equal. Vhіdnі straight lines to draw the point of the crossbar M . How to designate a kut, what is joking (significantly yogo α) between straight lines?
Let's look at the formulation of the main principle of the importance of Kuta in the minds of the task.
We know that straight lines are closely related to the concepts of such a concept, like a direct and normal vector. As far as we can equalize the current line, we can take the coordinates of these vectors from it. We can work together for two straight lines that overlap.
Kut, two direct denials that mingle, you can know for help:
- kuta mizh direct vectors;
- kuta mizh normal vectors;
- kuta between the normal vector of one straight line and the other direct vector.
Now let's look at the skin's way of okremo.
1. Assume that we have a straight line a with a direct vector a → = (a x , a y) і a straight line b with a direct vector b → (b x , b y) . Now we add two vectors a → and b → into the break point. If we care that the stench roztashovuvatimutsya skin on its own. Then we have є chotiri options for their mutual distribution. illustration:

If we cut between two vectors we are not stupid, then we will need a cut between straight lines a and b, which are intertwined. If you’re stupid, then kut, scho shkaєtsya, will be more kuta, summіzhny z kut a → , b → ^ . In this order, α = a → , b → ^ y timesі, so a → , b → ^ ≤ 90 ° , i α = 180 ° - a → , b → ^ , so a → , b → ^ > 90 ° .
Due to the fact that the cosines of the equal cuts are equal, we can rewrite the equals as follows: cos α = cos a → , b → ^ , so a → , b → ^ ≤ 90 ° ; cos α = cos 180 ° - a → , b → ^ = - cos a → , b → ^ , so a → , b → ^ > 90 ° .
Another vipadku had a vikoristano formula and a citation. in such a manner,
cos α cos a → , b → ^ , cos a → , b → ^ ≥ 0 - cos a → , b → ^ , cos a → , b → ^< 0 ⇔ cos α = cos a → , b → ^
We write the rest of the formula in words:
Appointment 3
The cosine of the kuta, made up of two straight lines that overlap, is equal to the modulus of the cosine of the kuta between the two direct vectors.
A wild looking formula for the cosine of kuta between two vectors a → = (a x, a y) і b → = (b x, b y) looks like this:
cos a → , b → ^ = a → , b → ^ a → b → = a x b x + a y + b y a x 2 + a y 2 b x 2 + b y 2
With it, we can introduce the formula for the cosine of kuta between two given lines:
cos α = a x b x + a y + b y a x 2 + a y 2 b x 2 + b y 2 = a x b x + a y + b y a x 2 + a y 2 b x 2 + b y 2
Todi kut itself can be known by the following formula:
α = a r c cos a x b x + a y + b y a x 2 + a y 2 b x 2 + b y 2
Here a → = (a x , a y) and b → = (b x , b y) are direct vectors of given lines.
Let's aim the butt of the task.
butt 1
In a rectangular coordinate system on the plane of the given two straight lines, which overlap, a і b . Їх can be described by parametric equalities x = 1 + 4 · λ y = 2 + λ ∈ R і x 5 = y - 6 - 3 . Calculate the cut between them with straight lines.
Solution
We have є parametric alignment, then, for tsієї straight lines, we can immediately write down the coordinates of the її direct vector. Therefore, it is necessary to take the value of the coefficients for the parameters, so. straight line x = 1 + 4 λ y = 2 + λ ∈ R
The other is directly described for the help of canonical alignment x5 = y-6-3. Here we can take the coordinates from the signs. In this order, tsya straight line can be a direct vector b → = (5, - 3) .
Dali we pass without a middle to the znakhodzhennya kuta. For which, we can simply represent the coordinates of two vectors y by invoking the formula α = a r cos a x · b x + a y + b y a x 2 + a y 2 · b x 2 + b y 2 . We take this:
α = a r c cos 4 5 + 1 (-3) 4 2 + 1 2 5 2 + (- 3) 2 = a r c cos 17 17 34 = a r c cos 1 2 = 45°
Vidpovid: given directly at 45 degrees.
We can solve a similar problem for additional knowledge of the Kuta between normal vectors. If we have a straight line a with a normal vector n a → = (n a x , n a y) і a straight line b with a normal vector n b → = (n b x , n b y) , then kut between them is more kutu m_zh n a → і n b → or kutu, which will be summable h n a →, n b → ^. The method of indications on the image:

The formulas for calculating the cosine of the kuta between the straight lines that overlap, and the kuta itself for the additional coordinates of the normal vectors look like this:
cos α = cos n a → , n b → ^ = n a x n b x + n a y + n b y n a x 2 + n a y 2 n b x 2 + n b y 2 α = a r c cos n a x n b x + n a y + n b y n a x 2
Here n a → і n b → designate the normal vectors of two direct assignments.
butt 2
For a rectangular coordinate system, two straight lines are set for an additional alignment 3 x + 5 y - 30 = 0 and x + 4 y - 17 = 0 . Find the sine, cosine of the kuta between them and the value of the kuta itself.
Solution
Include direct assignments with additional normal straight lines of the form A x + B y + C = 0 . The normal vector is meaningfully n → = (A, B). We know the coordinates of the first normal vector for one straight line and write їх: n a → = (3 , 5) . For the other straight line x + 4 y - 17 = 0 is the normal vector of coordinates n b → = (1, 4). Now let's add the value of the formula and fix the result:
cos α = cos n a → , n b → ^ = 3 1 + 5 4 3 2 + 5 2 1 2 + 4 2 = 23 34 17 = 23 2 34
As we know the cosine of the kuta, we can calculate its sine, which is basically trigonometrical. Oskіlki kut α, straight lines, not stupid, then sin α \u003d 1 - cos 2 α \u003d 1 - 23 2 34 2 \u003d 7 2 34.
For this time α = r c cos 23 2 34 = r c sin 7 2 34 .
Suggestion: cos α = 23 2 34 , sin α = 7 2 34 , α = a r c cos 23 2 34 = a r c sin 7 2 34
Let's take a look at the remaining slope - the significance of the kuta between the lines, as we are given the coordinates of the direct vector of one line and the other normal vector.
Assume that the line a can be a direct vector a → = (a x , a y) , and the line b is a normal vector n b → = (n b x , n b y) . We need to include vectors and breakpoints and look at all options for this mutual expansion. on the picture:

If the value of the cut between the given vectors is not more than 90 degrees, then it should be possible to add a cut between a and b to a direct cut.
a → , n b → ^ = 90 ° - α in that case, so a → , n b → ^ ≤ 90 ° .
If the fault is less than 90 degrees, then we take the step:
a → , n b → ^ > 90 ° , then a → , n b → ^ = 90 ° + α
Vikoristovuyuchi the rule of equivalence of cosinus of equal kutivs, we write down:
cos a → , n b → ^ = cos (90 ° - α) = sin α for a → , n b → ^ ≤ 90 °.
cos a → , n b → ^ = cos 90 ° + α = - sin α at a → , n b → ^ > 90 ° .
in such a manner,
sin α = cos a → , n b → ^ , a → , n b → ^ ≤ 90 ° -- cos a → , n b → ^ , a → , n b → ^ > 90 ° ⇔ sin α = cos a → , n b → ^ , a → , n b → ^ > 0 - cos a → , n b → ^ , a → , n b → ^< 0 ⇔ ⇔ sin α = cos a → , n b → ^
We formulate visnovok.
Appointment 4
To know the sine of kuta between two straight lines that overlap on the plane, it is necessary to calculate the modulus of the cosine of kuta between the direct vector of the first straight line and the normal vector of the other.
Let's write down the required formulas. Significance of the sine of the kuta:
sin α = cos a → , n b → ^ = a x n b x + a y n b y a x 2 + a y 2 n b x 2 + n b y 2
Knowledge of the kut itself:
α = a r c sin = a x n b x + a y n b y a x 2 + a y 2 n b x 2 + n b y 2
Here a → є is the direct vector of the first line, and n b → the normal vector of the other.
butt 3
Two straight lines that overlap are given by equals x - 5 = y - 6 3 x + 4 y - 17 = 0 . Find the cut of the peretina.
Solution
We take the coordinates of the direct and normal vectors from the given equalities. Enter a → = (- 5, 3) і n → b = (1, 4). We take the formula α = a r c sin = a x n b x + a y n b y a x 2 + a y 2 n b x 2 + n b y 2 i Important:
α = a r c sin = - 5 1 + 3 4 (- 5) 2 + 3 2 1 2 + 4 2 = a r c sin 7 2 34
Reveal the respect that we took equal care of the previous task and took away such a result, in a different way.
Suggestion:α = a r c sin 7 2 34
We will introduce one more way to determine the required quota for the help of the quotation coefficients of the direct tasks.
We have a straight line a , as given in a rectangular coordinate system for an additional alignment y = k 1 · x + b 1 і straight b , given as y = k 2 · x + b 2 . Price equalization of straight lines from the cut coefficient. To know the cut of the peretina, vikoristovuemo formula:
α = a r c cos k 1 · k 2 + 1 k 1 2 + 1 · k 2 2 + 1 de k 1 і k 2 For otrimannya tsgogo record bolo vikoristano formula vyznachennya kuta through the coordinates of the normal vectors.
butt 4
And the two are straight, which intertwine on the flat, assignments by peers y = - 3 5 x + 6 and y = - 1 4 x + 17 4 . Calculate the size of the cut of the peretina.
Solution
Kutovі coefіtsієnti of our direct doіvnyuyut k 1 = - 3 5 і k 2 = - 1 4 . Dodamo їх у formula α = a r c cos k 1 k 2 + 1 k 1 2 + 1 k 2 2 + 1
α = a r c cos - 3 5 - 1 4 + 1 - 3 5 2 + 1 - 1 4 2 + 1 = a r c cos 23 20 34 24 17 16 = a r c cos 23 2 34
Suggestion:α = a r c cos 23 2 34
In the visnovkas, which point should be indicated that the formulas for the significance of the kuta are introduced here, not necessarily to remember. For whom it is sufficient to know the coordinates of the straight lines and/or normal vectors in the given straight lines and to assign them to different types of equalities. And the axis of the formula for calculating the cosine of kuta is easier to remember and write down.
How to count the cuts between the straight lines
The calculation of such a cut can be reduced to the calculation of the coordinates of the direct vectors and the value of the cut made by these vectors. For such butts, the victorious ones themselves are mirrored, as if they were brought to the point.
Let's say that we can have a right-angled coordinate system, laid out in a trivial space. It has two lines a and b with a cross point M . To calculate the coordinates of the direct vectors, it is necessary to know the alignment of these lines. Significantly direct vectors a → = (a x, a y, a z) і b → = (b x, b y, b z). To calculate the cosine of the kuta between them, we speed it up with the formula:
cos α = cos a → , b → ^ = a → , b → a → b →
For the knowledge of the kut itself, we need this formula:
α = a r c cos a x b x + a y b y + a z b z a x 2 + a y 2 + a z 2 b x 2 + b y 2 + b z 2
butt 5
We may be straight, given in a trivial space for additional equalization x 1 = y - 3 = z + 3 - 2. It seems that it is overshadowed by the veil of Oz. Calculate the cut of the line and the cosine of that cut.
Solution
Significantly kut, which is required to be counted, with the letter α. We write down the coordinates of the direct vector for the first straight line - a → = (1, -3, -2). For the axis of applicability, we can take the coordinate vector k → = (0, 0, 1) as a direct one. We took away the necessary data and we can add them to the formula:
cos α = cos a → , k → ^ = a → , k → a → k → = 1 0 - 3 0 - 2 1 1 2 + (- 3) 2 + (- 2) 2 0 2 + 0 2 + 1 2 = 2 8 = 1 2
From the results we took away what we needed to cut the cost a r c cos 1 2 = 45 °.
Suggestion: cos α = 12, α = 45°.
How did you remember the pardon in the text, be kind, see it and press Ctrl + Enter
a. Let the data be given two straight lines, straight as it was assigned in division 1, to satisfy various positive and negative kuti, if you can, you can be both hospitable and stupid. Knowing one of these kutivs, we easily know the other.
Між іншим, in all of them, the numerical value of the tangent is one and the same, the difference can be less in the sign

Equation of straight lines. Numbers are projections of direct vectors on the first and other lines Kut between these vectors is closer to one of the kutivs, which are settled by straight lines. Therefore, the task is to lead up to the appointment of a kuta between vectors.
![]()
For simplicity, you can wash yourself under the hood between two people with direct understanding of the host of the positive hood (like, for example, Fig. 53).

Then the tangent of this cut will always be positive. In this way, as in the right part of the formula (1) we removed the minus sign, we are guilty of removing it in order to save only the absolute value.
butt. Designate cut between straight lines

For formula (1) we can
With. If it will be appointed, like on the side of the kuta є yogo cob and like a kіntsem, then, vіdrakhovuchi zavzhd directly kuta against the year's arrow, we can formula (1) win more. How unimportant to perekonatis іz fig. 53 the sign that appears at the right side of the formula (1) will be shown, which is the same - gostry or stupid - kut make a friend straight from the first.
(It is clear, from Fig. 53, we can see that between the first and other direct vectors, the opposite is true between the straight lines, or it is blown up by ±180 °.)
d. As straight lines are parallel, then parallel and straight vectors Zastosovuyuchi mental parallelism of two vectors is taken away!
![]()
The mind is necessary and sufficient for the parallelism of two straight lines.
butt. Straight
parallels, shards
![]()
e. If the lines are perpendicular, then their lines are vectors and also perpendicular. Zastosovuyuchi mental perpendicularity of two vectors we take away mental perpendicularity of two lines, and itself
butt. Straight
perpendicular through those
At the link with the minds of parallelism and perpendicularity, two tasks are about to come.
f. Draw a line through a point parallel to the given line
The solution is to be carried out in this way. Since the shukana is parallel to the given line, then for the її direct vector you can take the same one that the given line has, that is the vector with the projections A and B.
butt. Alignment of a straight line that passes through a point (1; 3) parallel to a straight line
be coming!
g. Draw a line through a point perpendicular to the given line
Here, for a direct vector, it is not suitable to take a vector with projections A i, but you need to take a vector that has perpendiculars. The projections of the vector can be chosen in such a way, as a result of the mental perpendicularity of both vectors, so as a mental perpendicularity
You can vikonati with your mind in an inconspicuous, impersonal way, to the fact that there is one and the same equal with two unknown. Ale, just take it, go. Then write directly at the form
butt. Alignment of a straight line to pass through a point (-7; 2) perpendicular to a straight line
be on the offensive (for another formula)!
h. In that mood, if the direct assignments are equal to the mind
rewriting qi equal otherwise, maybe
The skin schoolboy, who is preparing to EDI s mathematics, will repeat the topic “Knowledge of Kuta between straight lines” in a rough manner. As the statistics show, when passing the attestation test for a given division of stereometry, it is difficult for a large number of scientists. At the same time, you need to know the cut between straight lines, they are used in ЄDI as a basic one, as well as a profile level. Tse means that you can remember them.
Highlights
In the space there are 4 types of mutual distribution of straight lines. The stench can sbіgatisya, peretinatisya, be parallel, or such as to be shriveled. Kut mizh them can be gostrim chi straight.
For knowledge of the kuta between direct lines in ЄДІ or, for example, among the decided schoolchildren of Moscow and other places, they can win a few ways to solve problems according to this division of stereometry. Vikonati zavdannya can be a path of classical inspirations. For which variant, the main axioms of the theorem of stereometry. It is necessary for schoolchildren to remember logically to vibudovuvat mirkuvannya and create chairs in order to bring the task to a planimetric task.
You can also use the vector-coordinate method, zastosovuchi simple formulas, rules and algorithms. A smut in tsimu vipadku - correctly vikonati usі counting. Learn your skills in solving problems in stereometry and other divisions of the school course to help you with the enlightenment project "Shkolkove".
Appointment. If you set two lines y = k 1 x + b 1 , y = k 2 x + b 2 then the best cut between the lines will be
Two straight lines are parallel, so k1 = k2. Two straight lines are perpendicular, so k1 = -1/k2.
Theorem. Direct Ax + Vu + C \u003d 0 і A 1 x + B 1 y + C 1 \u003d 0 parallel, if the proportional coefficients A 1 \u003d A, B 1 \u003d B. If we have more C1 \u003d C, then they are straight. The coordinates of the cross point of two straight lines are changed as a decoupling of the system of alignments of straight lines.
Rivnyannya straight, scho to pass through given a point
Perpendicular to this line
Appointment. The straight line that passes through the point M 1 (x 1, y 1) i is perpendicular to the straight line y \u003d kx + b seems to be equal:

Walk from the point to the straight line
Theorem. If the point M (x 0, y 0) is given, then go up to the straight line Ax + Vy + C = 0
 .
.
Bringing. Let the point M 1 (x 1, y 1) be the basis of the perpendicular dropped from the point M on a given straight line. Walk between points M and M 1:
![]() (1)
(1)
The coordinates x 1 and 1 can be found as a solution to the alignment system:

Another alignment of the system is the alignment of a straight line, which passes through a given point M0 perpendicular to a given straight line. How to remake the first level of the system at a glance:
A(x - x 0) + B(y - y 0) + Ax 0 + By 0 + C = 0,
then, virishyuchi, otrimaemo:

Substituting qi virazi equal (1), we know:

The theorem has been completed.
butt. Designate cut between straight lines: y = -3 x + 7; y = 2 x +1.
k 1 \u003d -3; k2 = 2; tgφ =  ; φ = p /4.
; φ = p /4.
butt. Show that straight lines 3x - 5y + 7 \u003d 0 і 10x + 6y - 3 \u003d 0 are perpendicular.
Solution. We know: k 1 \u003d 3/5, k 2 \u003d -5/3, k 1 * k 2 \u003d -1, also, straight lines are perpendicular.
butt. Given the vertices of the tricot A(0; 1), B (6; 5), C (12; -1). Know the level of elevation drawn from the top Z.
Solution. We know the alignment of side AB:  ; 4 x = 6 y - 6;
; 4 x = 6 y - 6;
2x - 3y + 3 = 0;
Shukane equal height can look like: Ax + By + C = 0 or y = kx + b. k =. Then y =. Because height to pass through point C, її coordinates satisfy this alignment:  stars b = 17. Together: .
stars b = 17. Together: . 
Valid: 3 x + 2 y - 34 = 0.
Alignment of a straight line, to pass through this point in a straight line. Alignment of a straight line to pass through two given points. Kut mizh two straight lines. Umov's parallelism and perpendicularity of two lines. Designation of the cross point of two straight lines
1. Alignment of a straight line to pass through this point A(x 1 , y 1) for this one directly, which is marked by a cut coefficient k,
y - y 1 = k(x - x 1). (1)
The goal is to designate a pencil of lines that passes through a point A(x 1 , y 1), which is called the center of the beam.
2. Alignment of a straight line that passes through two points: A(x 1 , y 1) that B(x 2 , y 2), written like this:
The cut coefficient is direct, which passes through two given points, depends on the formula
3. Kutom between straight lines Aі B called kut, for which it is necessary to turn the persha straight A near the point of intersection of these lines against the turn of the Godinnikov's arrow to the bend of її with another straight line B. Like two direct assignments with equal coefficients
y = k 1 x + B 1 ,
y = k 2 x + B 2 , (4)
then the cut between them depends on the formula
Follow the respect for those who in the number book fraction from the top coefficient of the other straight line see the top coefficient of the first straight line.
Like a direct task for a savvy person
A 1 x + B 1 y + C 1 = 0,
A 2 x + B 2 y + C 2 = 0, (6)
cut between them depends on the formula
4. Wash the parallelism of two lines:
a) Even though direct tasks are equal (4) with a cut coefficient, then it is necessary enough mindїх parallelisms polgає in parity їх kutovykh coefficients:
k 1 = k 2 . (8)
b) For the viewpoint, if it is directly assigned by the equalities of the global view (6), it is necessary that sufficient intelligence is used to determine the parallelism in the fact that the coefficients in the case of the correct current coordinates of the equal proportions, tobto.
5. Think of the perpendicularity of two lines:
a) In times, if the direct assignments are equal (4) with the cut coefficient, it is necessary and sufficient for the mind to have the right perpendicularity in the fact that their cut coefficients are wrapped by the value and the length by the sign, tobto.
Tsya umova can be written down in the same way at the sight
k 1 k 2 = -1. (11)
b) Even if direct tasks are equal to the savage look (6), then the mind’s perpendicularity (necessary that sufficient) is equal to the visconna’s equal
A 1 A 2 + B 1 B 2 = 0. (12)
6. The coordinates of the cross point of two straight lines are known by arranging the alignment system (6). Straight (6) tinker in that and only in that vein, if
1. Write equal lines that pass through the point M, one of them is parallel, and the other is perpendicular to the given line l.



